建議您使用以下瀏覽器觀看本網站,
以獲得最佳瀏覽效果。
Semisynthesis
Panlabs utilizes microbial fermentation and enzymatic conversion technologies to produce precursors or intermediates of target compounds, which are then further refined through chemical synthesis to obtain the final products. Compared to traditional full chemical synthesis, this approach reduces the number of reaction steps and the use of organic solvents, thereby minimizing environmental impact. Panlabs provides gram-scale process optimization and supports customers in scaling up to commercial production, streamlining the overall workflow, reducing production costs, and enhancing efficiency and product quality.
Simplify synthesis steps
Reduce the use of organic solvents
Increase recovery rate and reduce impurities
Reduced costs
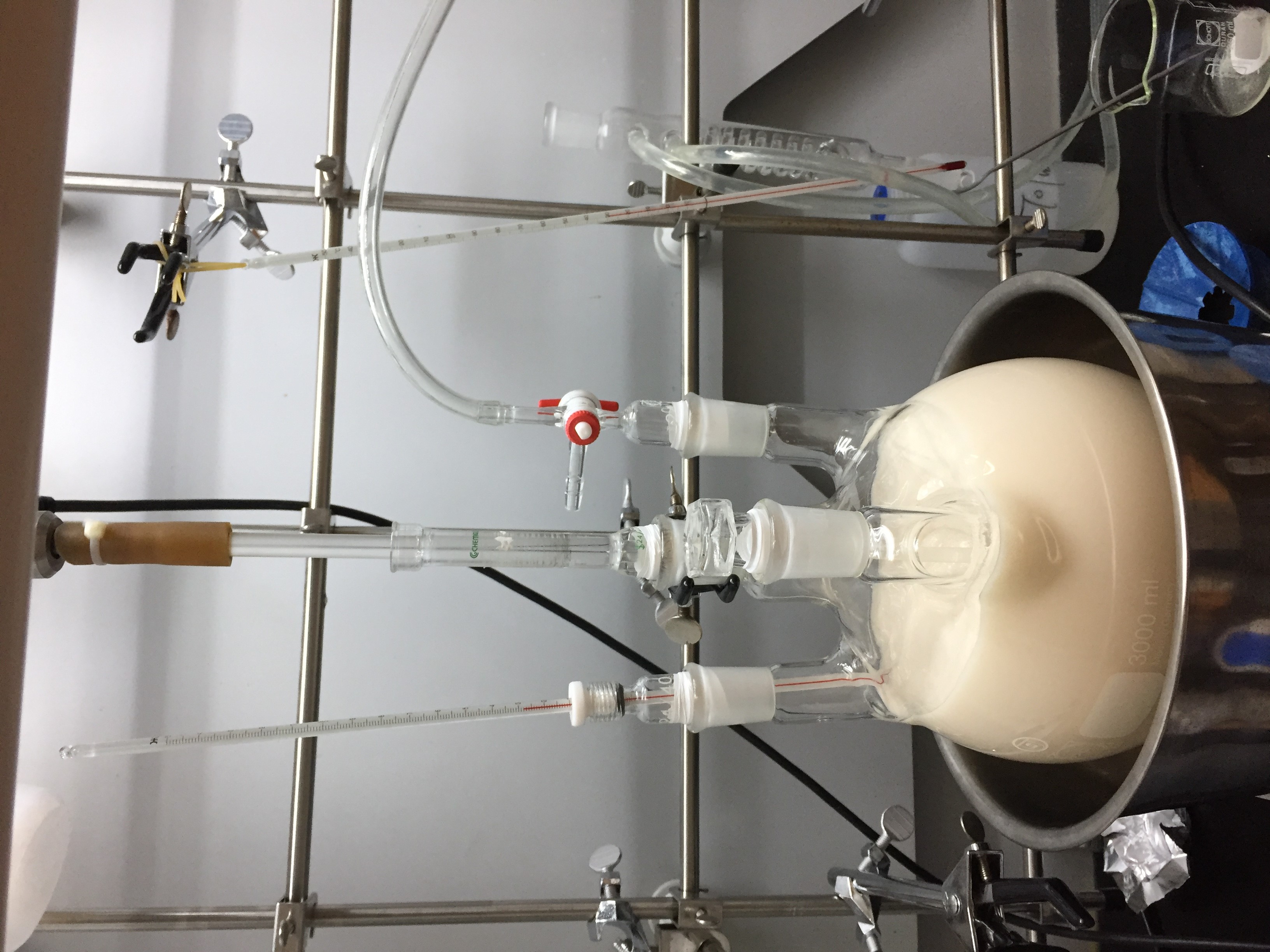
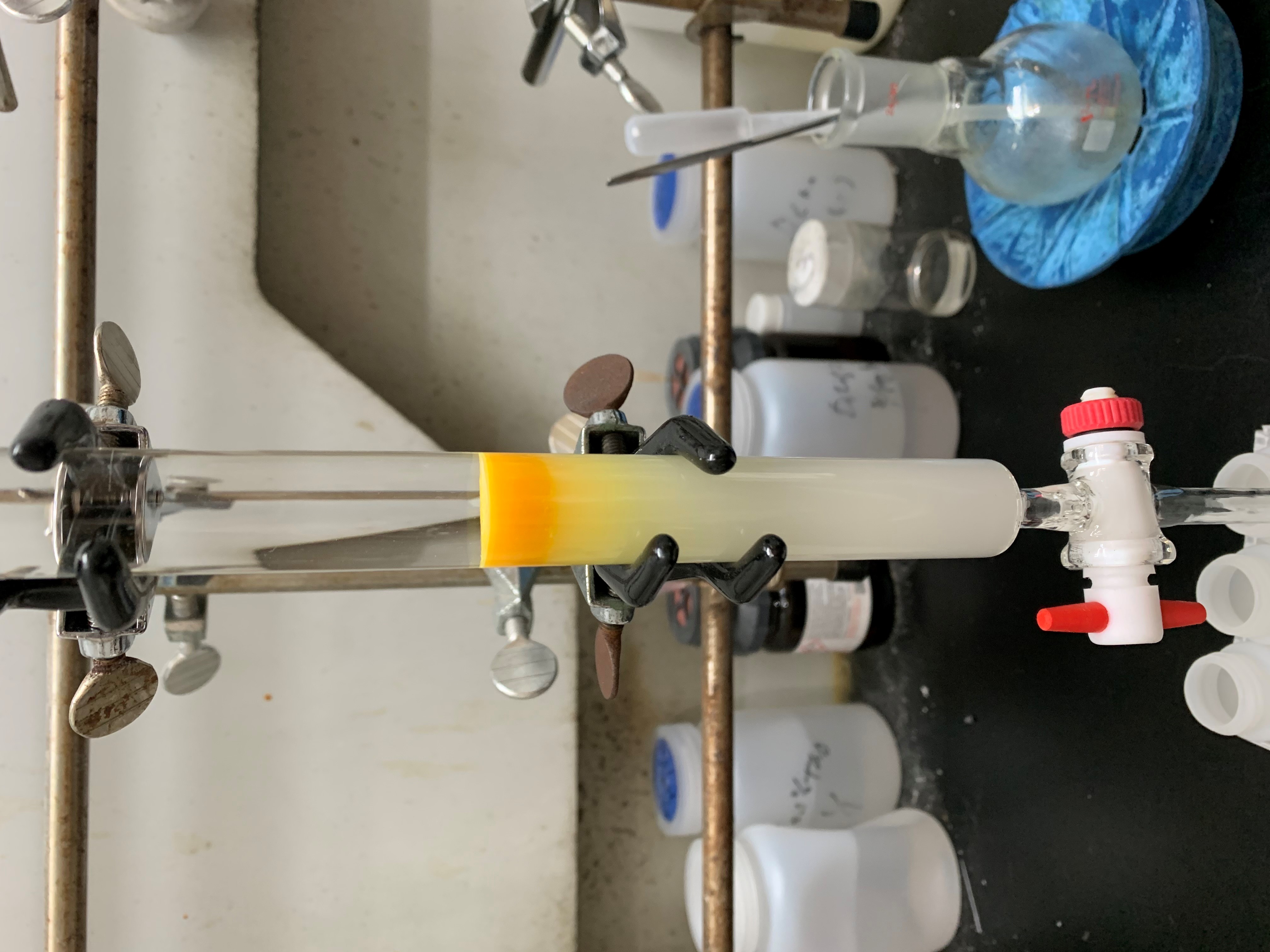
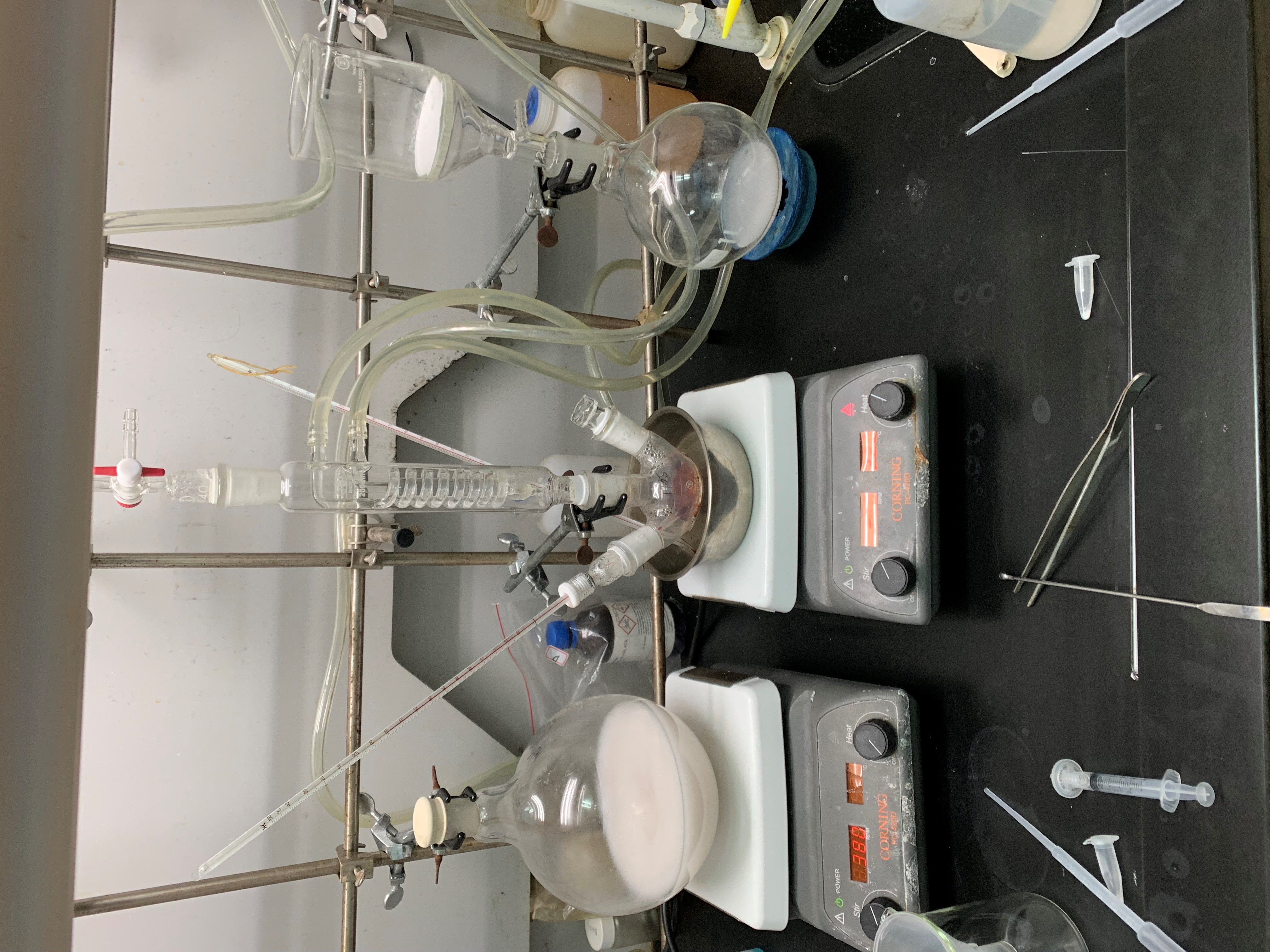
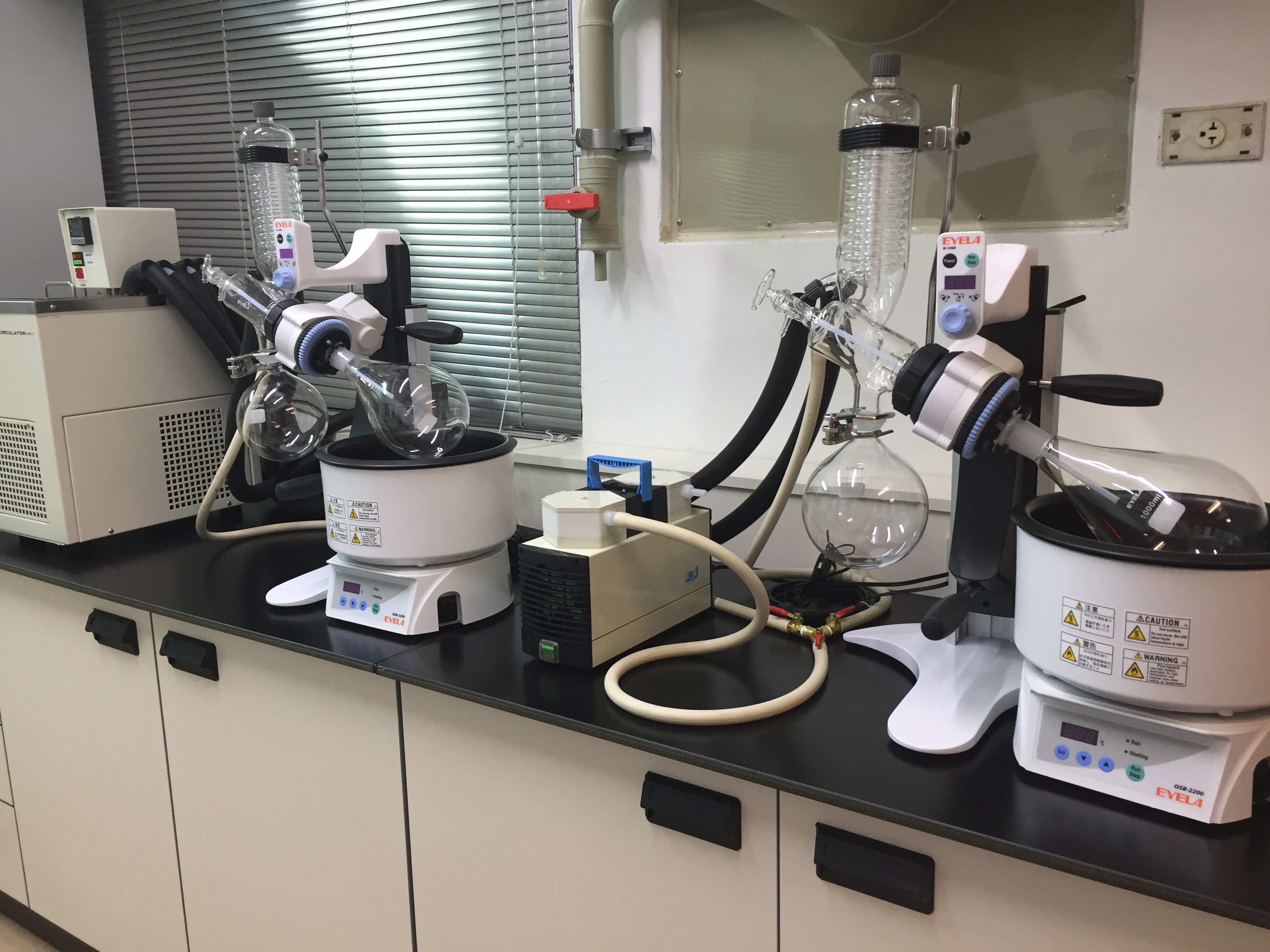
our equipment




OUR CASE
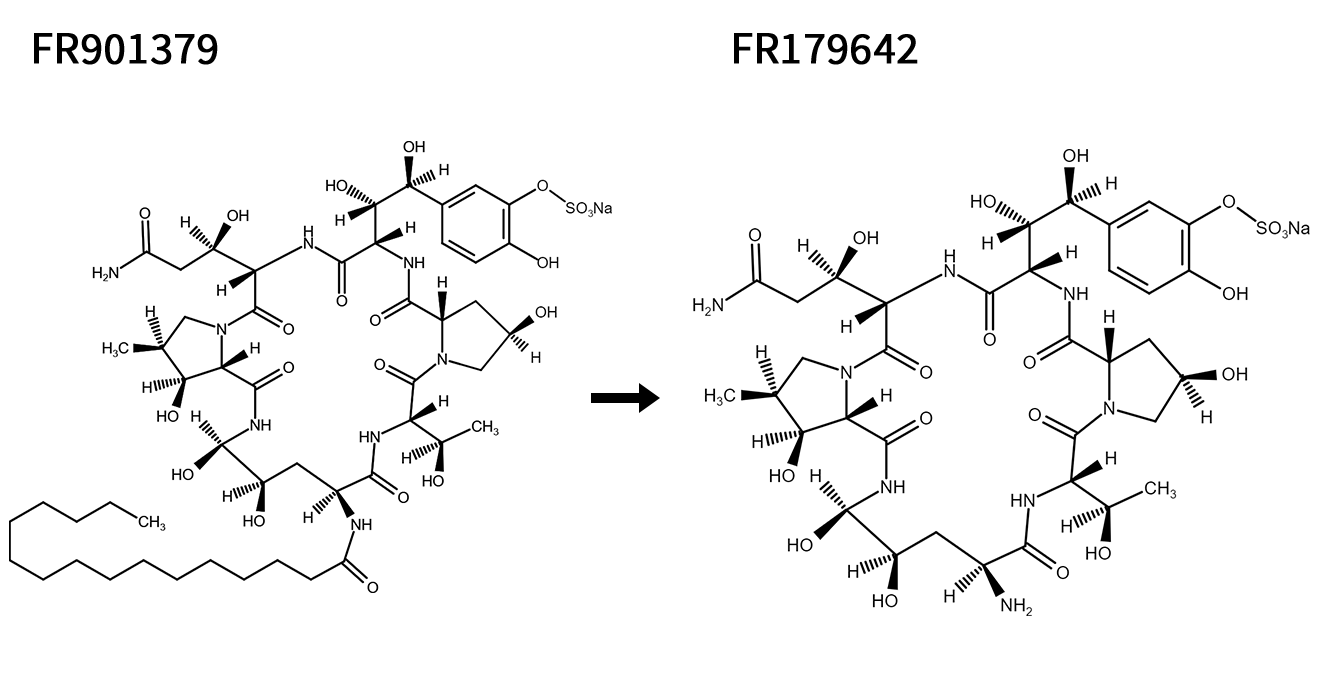
FR901379 → FR179642
FR179642 is a key intermediate in the synthesis of Micafungin, an Echinocandin-like antifungal drug that exerts its effects by inhibiting β-(1,3)-D-glucan synthesis, thereby compromising fungal cell wall integrity.
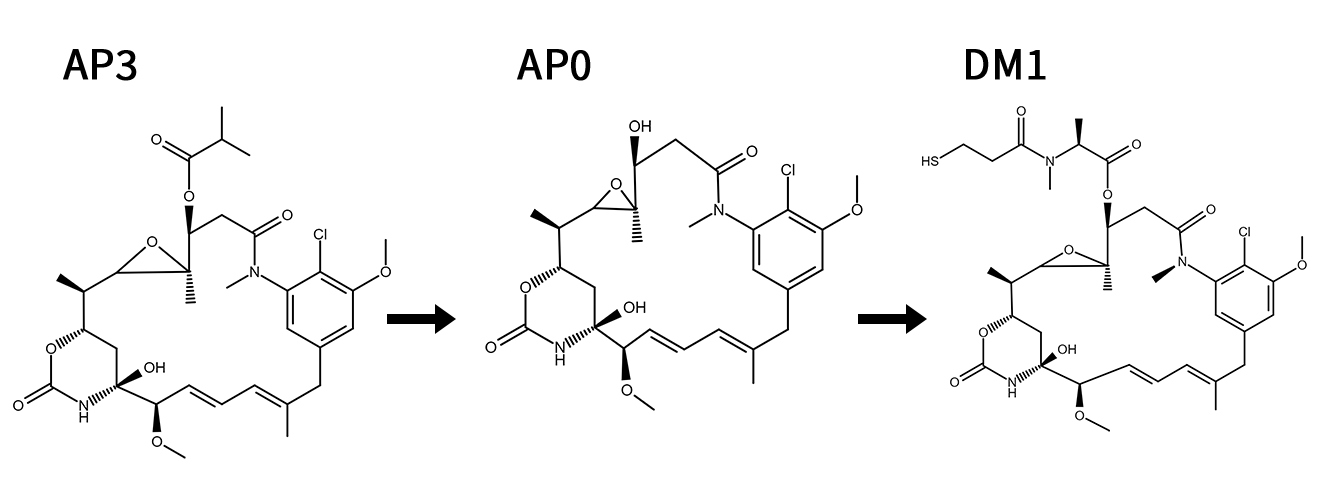
Ansamitocin P-3 (AP3) → Mertansine (DM1)
Mertansine (DM1) is the payload of antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs), a class of targeted cancer therapeutics. It delivers mertansine to tumor cells via antibody binding, releasing the toxin intracellularly to inhibit cell division and induce apoptosis.
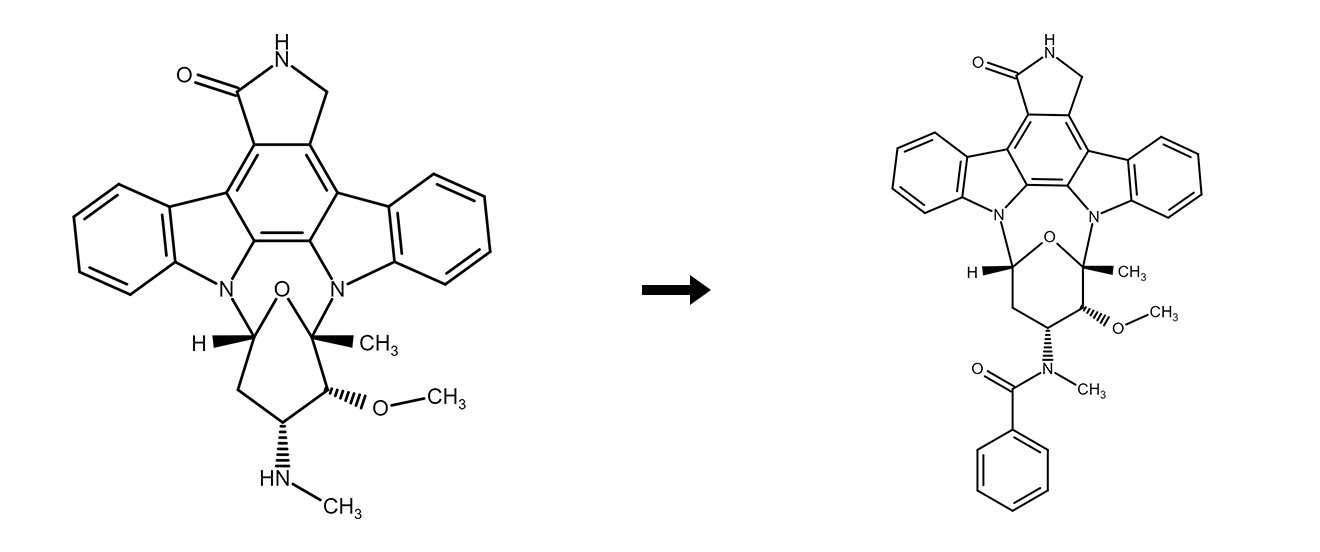
Staurosporine → Midostaurin
Midostaurin is a novel therapeutic agent derived from staurosporine, originally isolated from marine organisms. It acts as a multi-target kinase inhibitor, blocking the action of numerous receptor tyrosine kinases and disrupting signaling pathways essential for cell proliferation. Consequently, midostaurin exerts its anticancer effects by suppressing tumor growth or inducing apoptosis.
Calicheamicin γI → N-Acetyl-Calicheamicin
N-Acetyl-Calicheamicin is a highly potent cytotoxic agent belonging to the enediyne class of antibiotics. It exerts its antitumor activity by binding to DNA and inducing double-strand breaks, ultimately triggering apoptosis. Due to its high potency, N-Acetyl-Calicheamicin is primarily used as a payload in antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) for targeted cancer therapy.




